In 2024, bioinformatics has once again proven to be a cornerstone of innovation, driving discoveries that are reshaping our understanding of life at a molecular level. Did you know that the number of genetic variants uncovered this year alone surpassed expectations by millions? These breakthroughs are paving the way for revolutionary applications in healthcare, drug discovery, and beyond. Let’s delve into 10 of these fascinating breakthroughs!
#1 The Protein Revolution: Design on Demand
Traditionally, protein design has been a slow and laborious process. However, 2024 marked a paradigm shift with the emergence of AI-powered tools that can design proteins with desired properties. David Baker was awarded the 2024 Nobel Prize in Chemistry and was recognized for his groundbreaking work in computational protein design. His research enables the creation of entirely new proteins with novel functions, opening exciting possibilities in medicine, materials science, and nanotechnology.
#2 AlphaFold3: Unveiling the Molecular Mysteries
DeepMind’s AlphaFold3 was another monumental achievement, further advancing the capabilities of AI in molecular exploration. This version significantly improved upon its predecessor by offering more accurate predictions of protein structures across various biological contexts. Demis Hassabis and John Jumper, leading the DeepMind team, shared the Nobel Prize with David Baker for their contributions. The implications of AlphaFold3 extend to drug discovery and disease understanding, providing researchers with powerful insights into molecular biology.
#3 NIH’s All of Us Research Program: A Bonanza of Genetic Variants
The National Institutes of Health’s All of Us Research Program unveiled a treasure trove of over 275 million new genetic variants in 2024. This massive dataset provides a deeper understanding of human genetic diversity and its role in health and disease. This information will fuel the development of personalized medicine approaches, tailoring treatments to individual genetic profiles for improved efficacy.

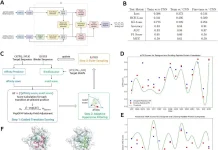
#4 Computing the Human Interactome: A Deep Dive into Protein Interactions
Proteins rarely work in isolation. They interact with each other to form intricate networks called the interactome. Understanding these interactions is crucial for deciphering cellular processes and disease mechanisms. In 2024, significant progress was made by the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, along with others, in computationally modeling the human interactome, allowing researchers to map protein-protein interactions on a large scale. This knowledge can be used to identify potential drug targets and develop new therapeutic strategies.

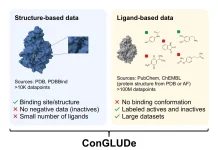
#5 RosettaFold All-Atom: Precision in Protein Modeling
RosettaFold All-Atom is a significant advancement made by researchers from the University of Washington in protein structure prediction, providing highly accurate models of protein structures at an atomic level. This level of detail is crucial for understanding protein function and designing novel therapeutics. RosettaFold All-Atom has opened new avenues for drug discovery, protein engineering, and the development of novel biomaterials.
#6 Unveiling Disease Before Symptoms: The Promise of Proteomic Signatures
Proteins are not static entities; their levels and modifications can change in response to disease. Researchers from the University of Cambridge and GSK Research and Development unveiled promising proteomic signatures capable of predicting over 60 diseases before symptoms manifest. This early detection capability could transform preventive medicine by allowing for timely interventions based on individual risk profiles.

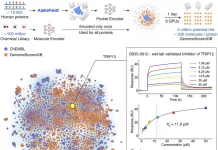
#7 Synthemol: AI vs. Superbugs – Designing Powerful Antibiotics
The fight against antibiotic resistance is a critical challenge in healthcare. In 2024, a new AI model called Synthemol emerged as a promising weapon in this battle. Synthemol, developed by Stanford University and McMaster University researchers, is a generative AI model specifically designed to discover novel antibiotics. By analyzing vast datasets of existing antibiotics and bacterial structures, Synthemol can create entirely new molecules with potent antibiotic properties, targeting drug-resistant pathogens identified by the World Health Organization as a significant global health threat. This technology has the potential to revolutionize our ability to combat drug-resistant bacteria and ensure the continued effectiveness of antibiotics in saving lives.
#8 Simulating Evolution with EvolutionaryScale’s ESM Models
EvolutionaryScale’s ESM models are revolutionizing our understanding of protein evolution. ESM Cambrian marks a groundbreaking achievement in understanding proteins at an unprecedented scale using unsupervised learning. By leveraging advanced language models, this study deciphers the evolutionary relationships and functional properties of proteins without requiring labeled data. This approach not only accelerates protein annotation but also opens new pathways for exploring the origins of life and the diversity of biological systems. The integration of AI in decoding protein structures and functions represents a transformative step in computational biology, offering immense potential for innovations in healthcare, biotechnology, and evolutionary studies.

#9 Multimodal AI: Unlocking New Dimensions in Biological Data Exploration
The emergence of multimodal AI systems, capable of processing and integrating information from diverse sources like text, images, and even protein structures, is revolutionizing bioinformatics research. These AI models can analyze complex biological datasets more comprehensively, leading to deeper insights into disease mechanisms, drug discovery, and the evolution of life. For example, multimodal AI can integrate genomic data with protein structures and clinical information to predict disease risk and personalize treatment plans. Integrating diverse data sources promises to unlock new dimensions in our understanding of biological systems.

Examples of such multimodal AI models include:
- ChatNT: This model can engage in conversations about biological concepts, answer questions about DNA, RNA, and proteins, and even generate summaries of scientific literature.
- Med-Gemini: A powerful large language model specifically designed for medical applications. Med-Gemini can process and understand medical text, images, and other data types, enabling it to assist in tasks such as diagnosis, treatment planning, and drug discovery.
- NVIDIA BioNeMo: This AI platform provides tools for developing and deploying AI models for drug discovery, protein engineering, and other biomedical applications.
- Evolutionary Scale Modeling (ESM): These models can analyze vast amounts of protein sequence data to reconstruct evolutionary relationships and predict the functional and structural properties of proteins, integrating sequence information with evolutionary history.
These examples demonstrate the growing power of multimodal AI in transforming bioinformatics research and accelerating the pace of scientific discovery.
Discover More about the AI Trends Bioinformaticians Need to Know in 2025!
#10 Team of AI-Made Scientists: A Groundbreaking System for Automating Scientific Discovery
This groundbreaking research from the University of Illinois, with others, demonstrated the potential of AI to automate scientific discovery. A team of AI-powered algorithms was developed to independently conduct scientific experiments, analyze data, and generate new hypotheses. This approach has the potential to accelerate scientific research by automating routine tasks and enabling researchers to focus on more complex and challenging problems.

Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While the advancements in bioinformatics offer immense potential, they also present significant challenges and ethical dilemmas. Issues such as data privacy, equitable access to technologies, and the potential misuse of AI-driven discoveries require careful consideration. As we integrate these tools into healthcare and research, it is crucial to address these challenges responsibly, ensuring that innovation benefits all and minimizes harm.
Conclusion
These discoveries represent just a glimpse of the remarkable progress made in bioinformatics in 2024. The discoveries reflect a remarkable convergence of AI technology and biological research, promising to reshape our understanding of health and disease significantly. As these innovations continue to evolve, they will undoubtedly lead to enhanced diagnostic tools, personalized treatments, and a deeper comprehension of biological systems.
What excites you most about these discoveries? Share your thoughts and join the conversation as we shape the future of bioinformatics together!
Note: This is a list of some of the most exciting bioinformatics discoveries; it is not a ranking article.
Article Sources:
- The Protein Revolution: 2024 Nobel Prize in Chemistry Pioneers Protein Design and AI-Powered Predictions. Article
- The Ultimate Molecular Explorer: AlphaFold 3, DeepMind’s AI Marvel to Unravel the Mysteries of All Life’s Molecules. Article | Paper
- NIH’s All of Us Research Program Unveils 275 Million New Genetic Variants, Boosting Precision Medicine Efforts. Article | Paper
- Team of AI-made Scientists: A Groundbreaking System for Automating Scientific Discovery. Article | Paper
- Computing the Human Interactome: A Deep Dive into Protein Interactions. Article | Paper
- Unveiling Disease Before Symptoms: The Promise of Proteomic Signatures for Predicting Over 60 Diseases. Article | Paper
- Evolutionary Scale’s ESM Cambrian: Revolutionizing Protein Understanding at the Scale of Life with Unsupervised Learning. Article | Paper
- AI vs. Superbugs: A New Generative AI Model ‘SyntheMol’ Designs Powerful Antibiotics to Fight Resistant Bacteria. Article | Paper
- Exploring the Boundless Frontiers of Biomolecular Modeling and Design with RoseTTAFold All-Atom. Article | Paper
- Unveiling ChatNT: The Conversational AI Revolutionizing How We Explore DNA, RNA & Proteins. Article | Paper
- A New Era of AI in Medicine: Google’s Med-Gemini Sets New Standards. Article | Paper
- BioNeMo Folds the Human Proteome: A Fused Dataset of 3D Protein Models for Machine Learning Applications. Article | Paper
Important Note: arXiv & bioRxiv release preprints that have not yet undergone peer review. As a result, it is important to note that these papers should not be considered conclusive evidence, nor should they be used to direct clinical practice or influence health-related behavior. It is also important to understand that the information presented in these papers is not yet considered established or confirmed.
Follow Us!
Learn More:
Dr. Tamanna Anwar is a Scientist and Co-founder of the Centre of Bioinformatics Research and Technology (CBIRT). She is a passionate bioinformatics scientist and a visionary entrepreneur. Dr. Tamanna has worked as a Young Scientist at Jawaharlal Nehru University, New Delhi. She has also worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow at the University of Saskatchewan, Canada. She has several scientific research publications in high-impact research journals. Her latest endeavor is the development of a platform that acts as a one-stop solution for all bioinformatics related information as well as developing a bioinformatics news portal to report cutting-edge bioinformatics breakthroughs.