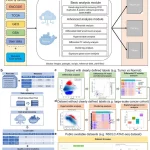
Amazon Omics is a purpose-built service from Amazon Web Services (AWS) that enables customers to store, query, and analyze genomic and biological data at scale. It offers fast, secure, and cost-effective storage, access, and analysis of large datasets, allowing customers to gain insights from their data and accelerate research quickly. Amazon Omics is designed to help customers reduce the time and cost associated with storing and analyzing large genomic datasets. Amazon Omics offers a range of tools and services, such as analytics and machine learning, to help customers analyze and gain insights from their genomic data.
There is no need to purchase specialized infrastructure or workflows to store and analyze genomic data because the cloud-based platform provides security, scalability, and the processing power needed.
The Amazon Web Services service uses artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and other AWS products and services to run IT-heavy bioinformatics workflows at the point of care and help patients identify the best treatment or prevention options.
Amazon OMICS – The Latest in Biological Big Data
Biological data is collected by healthcare and life sciences organizations to improve patient care. A number of these organizations use genetic profiling to map an individual’s genetic predisposition to disease, identify new drug targets by examining the structure and function of proteins, profile tumors by observing the genes expressed in a particular cell, or investigate how gut bacteria influence human health. It is often the case that these studies are collectively referred to as “omics.”
Over the past decade, AWS has helped healthcare and life sciences organizations accelerate data translation into actionable insights. Ancestry, AstraZeneca, DNAnexus, Genomics England, and GRAIL are among the companies that leverage AWS to improve security and reduce costs while accelerating the time to discovery.
This scale, which can be many petabytes, adds complexity to data access, processing, and tooling. There is a need for a cost-efficient and convenient means of storing omics data that is easy to retrieve and easy to use. Keeping accuracy and reliability while scaling across millions of samples is critical. To predict diseases, users also need specialized tools to analyze genetic patterns across populations.
Now, with Amazon OMICS, clinicians can query thousands of variants across multiple genes simultaneously to understand better how genomic variation, when combined with corresponding clinical data, may impact human health or determine clinical outcomes, according to AWS’ announcement.
The company announced the general availability of its Amazon Omics service, a tool designed to assist bioinformaticians, scientists, and researchers in storing, querying, and analyzing genomic, transcriptomic, and other omics data in order to improve health and advance scientific discovery.
In the Omics console, users can import and normalize petabytes of data into formats that are optimized for analysis with just a few clicks. Using Amazon Omics, researchers can prepare and analyze omics data with scalable workflows and integrated tools and automatically provision and scale the cloud infrastructure that underlies the omics data as needed. The researchers can focus on translating discoveries into diagnostics and therapies.
There are three primary components that make-up Amazon Omics:
- Affordable, omics-optimized object storage for storing and sharing data.
- In the context of bioinformatics workflows, managed computing allows customers to run the exact analysis they specify without having to worry about the underlying infrastructure and the provisioning of servers.
- Optimized data storage for population-scale analysis of variance.
The Registry of Open Data on Amazon Web Services allows users to combine their genomic data with other publicly available reference datasets, including the 1000 Genomes Project, which serves as a control to comprehend the risk of disease; the Genome Aggregation Database (gnomAD), which incorporates disease frequency data to enhance disease detection; and more than 60 other genomic datasets.
For DNA sequencing analyses, raw genomic variants can be searched in the form of “Variant Call Files (VCF)” to find results like faulty genes that produce cancer-causing proteins.
With Amazon Omics, the users can import their VCFs into a Variant Store and seamlessly convert that into a query-ready schema that is produced into an Apache Iceberg Table, available via the Variant Store. Additionally, it supports the import of variant annotations into an Annotation Store so that users can add their annotations.
In the context of the AWS ecosystem, partners like Lifebit and Ovation have access to large genomics data stores faster, allowing them to accelerate their work and create innovative biomedical data solutions.
Concluding Remarks
Amazon Omics is a managed service that allows you to quickly analyze large-scale omic data, like human genome samples, in hours instead of weeks. It comes with tutorials and SageMaker notebooks to help you get started.
Article Source: Reference Article 1 | Reference Article 2
Learn More:
Top Bioinformatics Books ↗
Learn more to get deeper insights into the field of bioinformatics.
Top Free Online Bioinformatics Courses ↗
Freely available courses to learn each and every aspect of bioinformatics.
Latest Bioinformatics Breakthroughs ↗
Stay updated with the latest discoveries in the field of bioinformatics.
Dr. Tamanna Anwar is a Scientist and Co-founder of the Centre of Bioinformatics Research and Technology (CBIRT). She is a passionate bioinformatics scientist and a visionary entrepreneur. Dr. Tamanna has worked as a Young Scientist at Jawaharlal Nehru University, New Delhi. She has also worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow at the University of Saskatchewan, Canada. She has several scientific research publications in high-impact research journals. Her latest endeavor is the development of a platform that acts as a one-stop solution for all bioinformatics related information as well as developing a bioinformatics news portal to report cutting-edge bioinformatics breakthroughs.