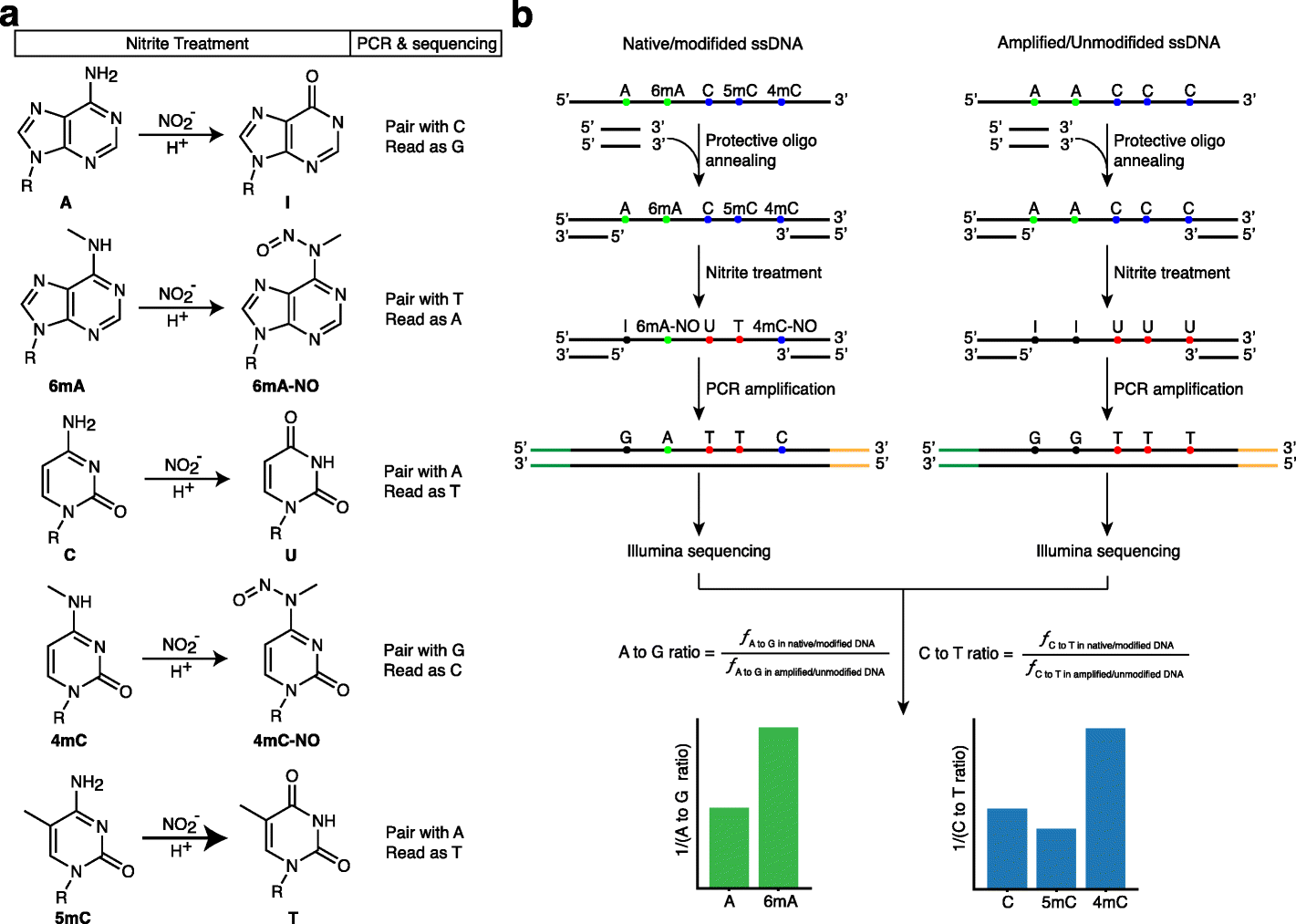
Baylor College of Medicine researchers introduce a new sequencing technique ‘NT-seq’ for simultaneously mapping all three forms of DNA methylation. All known methylation motifs in Escherichia coli and Helicobacter pylori genomes were reliably detected by NT-seq, which may also be utilized to find de novo methylation motifs. NT-seq offers a quick and effective way for genome-wide mapping of different types of DNA methylation.
Image Source: https://blogs.bcm.edu/2022/06/30/from-the-labs-new-method-boosts-the-study-of-regulation-of-gene-activity/
The DNA that determines whether genes are switched on or off can be chemically modified in minute amounts by cells in order to alter the activity of their genes. One of these alterations or tags in chemistry is the methyl group. DNA methylation in bacteria is thought to control virulence, reproduction, and gene expression. While in other organisms, including humans, DNA methylation is important for regulating the tissue-specific gene expression that establishes a cell’s identity, such as whether it is a skin cell or a brain cell.
DNA methylation study is a part of the field of epigenetics. According to corresponding author Dr. Tao Wu, assistant professor of molecular and human genetics at Baylor College of Medicine, it is important because it explains how a normal cell can change and create disease or why a specific type of bacteria causes a disease to be more severe than another, such as cancer.
The Wu Lab focuses on cancer epigenetics. The long-term objective of the research group is to comprehend the role of epigenetics in cancer better and to overcome therapeutic resistance to cancer.
Types of DNA Methylation
There are three types of DNA methylation in bacteria. The one that marks the DNA nucleotide or building block adenine is the most popular (N6-methyladenine or 6mA). The other two identify cytosine as a DNA base (N4-methylcytosine or 4mC and 5-methylcytosine or 5mC).
DNA Methylation Profiling Methods
Despite the fact that there are numerous approaches to study DNA methylation, Wu claimed that few techniques can successfully map all three forms of DNA methylation at once. However, 6mA is the most common form of methylation in prokaryotes. The majority of next-generation genomic sequencing (NGS) techniques for DNA methylation mapping have been developed for 5mC, such as bisulfite sequencing.
Although numerous antibody- or enzyme-based strategies have been created, these techniques are either difficult, low resolution, or limited to specific enzyme-cutting patterns.
Although DNA methylation motifs in bacterial genomes have been discovered using 3rd-generation single-molecule real-time sequencing (SMRT-seq), the present SMRT-seq lacks open-source bioinformatics tools or independent techniques that may cross-validate the results.
It was once believed that humans and other non-bacterial species mostly used methyl-cytosine tags, or the 5mC, to control gene activation. But in 2016, Wu along with his supervisor group at Yale University published a study in Nature revealing that DNA 6mA is also found in mammals. This discovery created a whole new range of opportunities for the research of cancer epigenetics.
The traditional methods to study the 5mC do not capture the adenine methylation in mammalian tissues. This motivated us to develop a novel method to profile not only 6mA but also 4mC and 5mC.
Dr. Tao Wu
NT-Seq—Nitrite Treatment Followed by Next-Generation Sequencing
Wu and his coworkers report the development of a chemical-based sequencing method to simultaneously quantify many epigenetic markers in the current study, which was published in the journal Genome Biology.
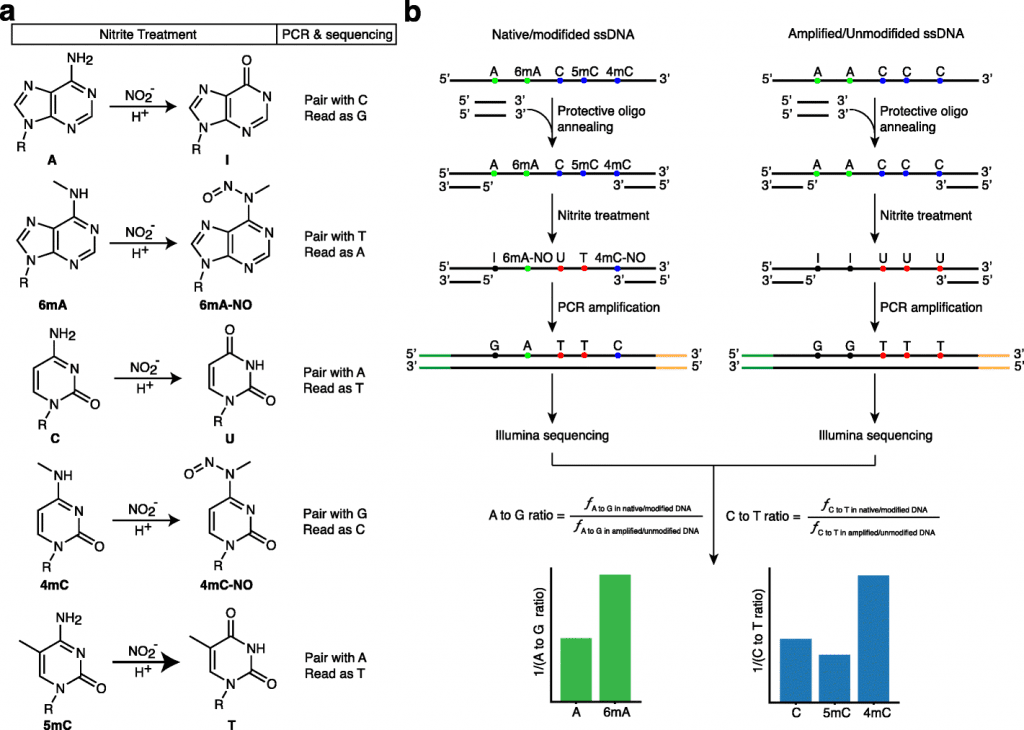
Image Source: NT-seq: a chemical-based sequencing method for genomic methylome profiling
The researcher’s approach, dubbed NT-seq—nitrite treatment followed by next-generation sequencing—is a sequencing technique for genome-wide mapping of different types of DNA methylation. Additionally, the method can amplify small clinical samples, which is something that other technologies cannot achieve.
The researchers demonstrated that bacterial and non-bacterial cells, including mammalian cells, can detect 6mA, 4mC, and 5mC using NT-seq. When compared to other techniques for genome-wide mapping of DNA methylation, NT-seq is effective, rapid, affordable, and has good resolution. Some of its drawbacks are specific to the unique composition of some genomes. In the study, the researchers offer recommendations for how to get around this restriction.
According to Wu, NT-seq can reveal new DNA methylation patterns or motifs, validate results produced by other methods, generate datasets for making machine-learning tools for the analysis of methylation, and lays the foundation to further the epigenetic study of genomic DNA 6mA in non-bacterial organisms, including studies on the epigenetics of cancer.
Story Source: Li, X., Guo, S., Cui, Y. et al. NT-seq: a chemical-based sequencing method for genomic methylome profiling. Genome Biol 23, 122 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-022-02689-9 https://blogs.bcm.edu/2022/06/30/from-the-labs-new-method-boosts-the-study-of-regulation-of-gene-activity/
Learn More About Bioinformatics:
Top Bioinformatics Books ↗
Learn more to get deeper insights into the field of bioinformatics.
Top Free Online Bioinformatics Courses ↗
Freely available courses to learn each and every aspect of bioinformatics.
Latest Bioinformatics Breakthroughs ↗
Stay updated with the latest discoveries in the field of bioinformatics.
Dr. Tamanna Anwar is a Scientist and Co-founder of the Centre of Bioinformatics Research and Technology (CBIRT). She is a passionate bioinformatics scientist and a visionary entrepreneur. Dr. Tamanna has worked as a Young Scientist at Jawaharlal Nehru University, New Delhi. She has also worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow at the University of Saskatchewan, Canada. She has several scientific research publications in high-impact research journals. Her latest endeavor is the development of a platform that acts as a one-stop solution for all bioinformatics related information as well as developing a bioinformatics news portal to report cutting-edge bioinformatics breakthroughs.