In the rapidly evolving field of single-cell biology, accurately identifying cell types from complex datasets remains a cornerstone of research. A team of scientists from Nanjing University, Inner Mongolia Minzu University, and Zhejiang University in China has developed CellReasoner, a groundbreaking artificial intelligence tool designed to streamline this process. This work introduces a lightweight, open-source large language model (LLM) that combines precision, interpretability, and adaptability, promising to transform how researchers analyze cellular data.
The Challenge of Cell Type Annotation
Understanding and interpreting a single cell type is a meticulous task that involves contemplating gene expression matrices, marker genes, and reference databases for precise integration. Traditional workflows do not differ from manual curation or rely on heavy computation models, which need enormous amounts of time, money, and offer little interpretability. While general-purpose LLMs like GPT-4 offer some benefits, their opacity and incredible resource costs make them prohibitively expensive and impractical for biomedical research purposes.
CellReasoner: A Reasoning-Enhanced LLM
CellReasoner was designed to overcome these limitations by providing a lightweight, open-source solution tailored for single-cell type annotation. Its consumer-grade GPU requirements encourage use among more laboratories, making it easier to access for more intricate studies. Unlike common models, CellReasoner places primary importance on advanced reasoning by employing step-wise inference known from experts to merge context-specific features and prior biological knowledge into strong classification models.
The CRAFT Training Strategy
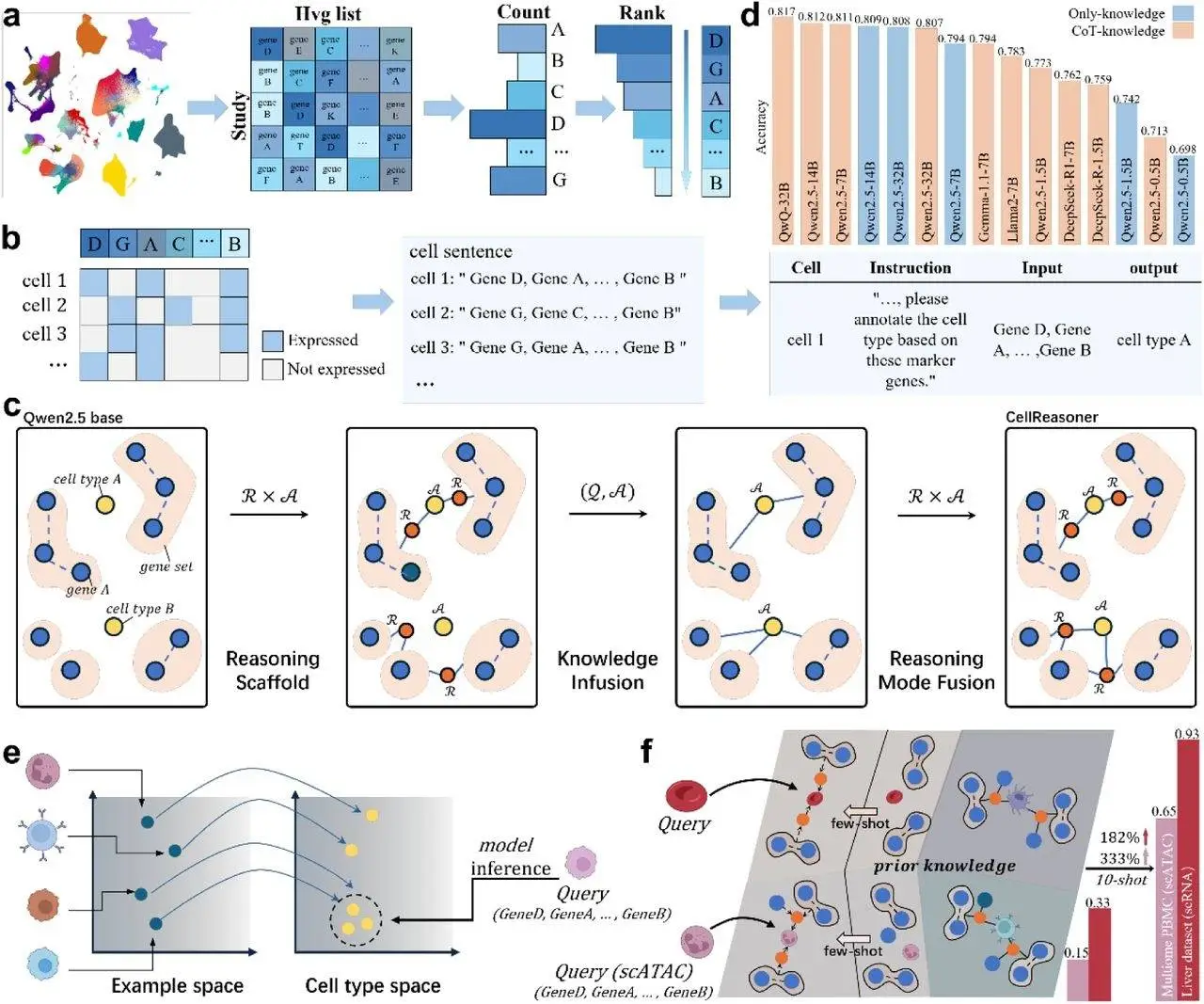
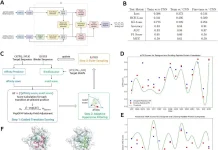
One of the key innovations in Cell Reasoner is its three-stage CRAFT (Cell Reasoning and Annotation Fusion Training) framework. The first step, the reasoning scaffold, teaches the model step-wise reasoning by using a small, yet high-quality set of exemplars that reflect chain-of-thought walkthroughs, akin to how human experts dissect marker genes. Stage two, knowledge infusion, embeds a wider corpus of biological literature for cross-referencing in relation to the model understanding of cell types and gene relationships. Reasoning mode fusion is the third stage, where the model is further tuned to retain reasoning capabilities alongside the newly integrated biological knowledge to ensure accuracy, interpretability, and explainability.
To standardize the informational input to be consistent and rich, CellReasoner utilizes “cell sentences,” which represent each cell’s gene expression profile in natural language style. The sentences are crafted by encoding highly variable genes in a predetermined order. This enables the model to execute cell-level reasoning and annotation without reference databases or labeled data.
Benchmarking and Performance
CellReasoner was systematically tested on a number of datasets, such as pancreatic cancer (PDAC), peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC3K), and liver tissue. The model was found to have superior performance compared to both generic LLMs and even domain-specific models in terms of accuracy and subtype fragmentation. For example, on the PDAC subset, CellReasoner achieved 0.73 accuracy alongside smaller models, outdoing larger models that had a higher computational cost. The model also showed great generalization by adapting to new tissue types and different data modalities, such as scATAC-seq, with little fine-tuning. Such rapid adaptability is important in real-life scenarios where researchers are likely to encounter novel cell types or heterogeneous datasets.
A distinguishing aspect of CellReasoner is its interpretability. The model provides marker-by-marker reasoning chains, detailing how it arrives at each annotation. This transparency not only builds trust in the model’s predictions but also helps researchers understand the underlying biology, potentially revealing new insights into cellular function and identity. In these tests, CellReasoner demonstrated expert-level reasoning by providing logical and accurate explanations alongside persuasive proof of complex cell type identity.
Conclusion
CellReasoner represents a significant advance in the application of AI to single-cell biology. By combining efficient reasoning, expert-level annotation, and practical accessibility, it offers a powerful tool for researchers seeking to unravel the complexities of cellular diversity. The model’s robust performance across diverse datasets and modalities, along with its transparent reasoning process, positions it as a valuable asset for the future of biomedical research.
Article Source: Reference Paper
Disclaimer:
The research discussed in this article was conducted and published by the authors of the referenced paper. CBIRT has no involvement in the research itself. This article is intended solely to raise awareness about recent developments and does not claim authorship or endorsement of the research.
Important Note: bioRxiv releases preprints that have not yet undergone peer review. As a result, it is important to note that these papers should not be considered conclusive evidence, nor should they be used to direct clinical practice or influence health-related behavior. It is also important to understand that the information presented in these papers is not yet considered established or confirmed.
Follow Us!
Learn More:
Anchal is a consulting scientific writing intern at CBIRT with a passion for bioinformatics and its miracles. She is pursuing an MTech in Bioinformatics from Delhi Technological University, Delhi. Through engaging prose, she invites readers to explore the captivating world of bioinformatics, showcasing its groundbreaking contributions to understanding the mysteries of life. Besides science, she enjoys reading and painting.