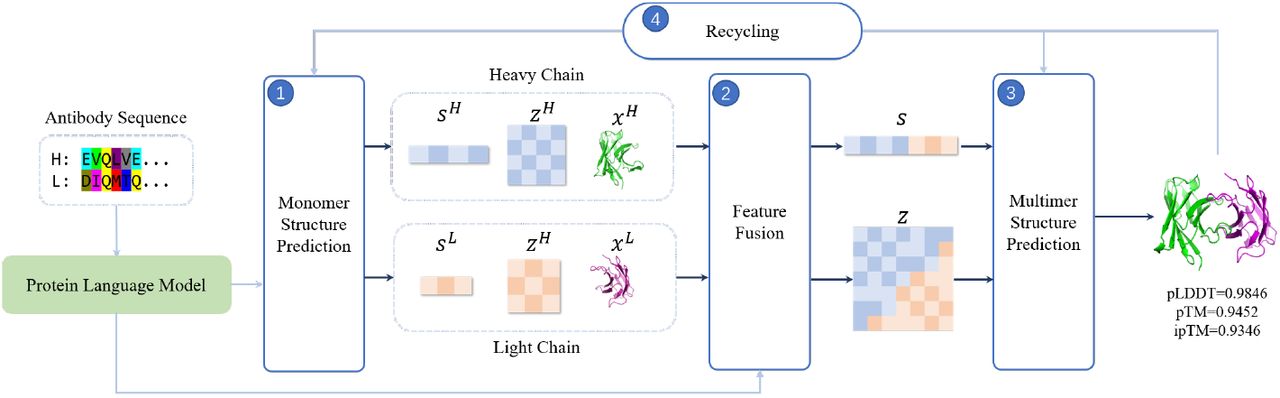
Antibodies are crucial components of the immune system, and their structure is critical for their function. Predicting the three-dimensional structure of antibodies without the use of sequence homologs has been a major challenge for researchers in the field of immunology. However, a research team from the University of California, San Francisco, has developed a new method called tFold-Ab that can predict the structure of antibodies and nanobodies with high accuracy and in a fraction of the time required by other methods. This is a significant advancement in the field and has the potential to provide valuable insights into the structure and function of antibodies, as well as their potential therapeutic applications.
Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system that are crucial for protecting the body against infections and other foreign invaders. They are highly specific and are able to recognize and bind to specific targets, such as viruses or bacteria. The structure of antibodies is critical for their function, and understanding this structure can provide valuable insights into their role in the immune system and the development of new therapies.
Traditionally, the structure of antibodies has been determined using X-ray crystallography, in which the crystal structure of the antibody is determined using X-ray diffraction. However, this method is time-consuming and requires large amounts of purified protein, making it difficult to apply to many antibodies. In addition, many antibodies do not have homologous sequences in databases, making it difficult to use traditional methods for structure prediction.
To address these challenges, researchers have developed tFold-Ab, which uses a combination of machine learning and physical simulation to predict the three-dimensional structure of antibodies and has been shown to be highly accurate and efficient.

Image Source: https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.11.10.515918
One of the key advantages of tFold-Ab is its speed and accuracy. In tests, tFold-Ab was able to predict the structures of antibodies with high accuracy and in fractions of the time required by other methods. This makes it a valuable tool for researchers and it has the potential to provide valuable insights into the role of antibodies in the immune system and the development of new therapies.
Another advantage of tFold-Ab is its ability to predict the structures of antibodies without the need for sequence homologs. This is important because many antibodies do not have homologous sequences in databases, making it difficult to use traditional methods for structure prediction. By using tFold-Ab, researchers can predict the structures of these antibodies, providing valuable insights into their function and potential therapeutic applications.
In addition to its speed and accuracy, tFold-Ab has other advantages that make it a valuable tool for researchers. For example, the method is able to predict the structures of both heavy and light chain antibodies, providing a comprehensive view of the antibody structure. In addition, tFold-Ab can predict the structures of antibodies with a wide range of lengths and sequences, making it applicable to a wide range of antibodies.
In conclusion, tFold-Ab is a valuable tool for predicting the structure of antibodies and nanobodies without the need for sequence homologs. Its speed and accuracy make it a valuable resource for researchers, and its ability to predict the structures of non-homologous antibodies is a major advancement in the field. Although the current model shows promising preliminary results, there is still room for improvement.
Article Source: Reference Paper | Web Server: tFold-Ab
Learn More:
Top Bioinformatics Books ↗
Learn more to get deeper insights into the field of bioinformatics.
Top Free Online Bioinformatics Courses ↗
Freely available courses to learn each and every aspect of bioinformatics.
Latest Bioinformatics Breakthroughs ↗
Stay updated with the latest discoveries in the field of bioinformatics.
Dr. Tamanna Anwar is a Scientist and Co-founder of the Centre of Bioinformatics Research and Technology (CBIRT). She is a passionate bioinformatics scientist and a visionary entrepreneur. Dr. Tamanna has worked as a Young Scientist at Jawaharlal Nehru University, New Delhi. She has also worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow at the University of Saskatchewan, Canada. She has several scientific research publications in high-impact research journals. Her latest endeavor is the development of a platform that acts as a one-stop solution for all bioinformatics related information as well as developing a bioinformatics news portal to report cutting-edge bioinformatics breakthroughs.
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar
- Dr. Tamanna Anwar