A ground-breaking solution in modern-day continuously advancing healthcare internationally is developing waves in vaccine improvement. Developed by brilliant minds at the School of Medicine, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, VaccineDesigner affords a powerful platform for epitope-based vaccine layout. It’s poised to convert how we tackle infectious diseases and address worldwide health challenges.
Unveiling VaccineDesigner
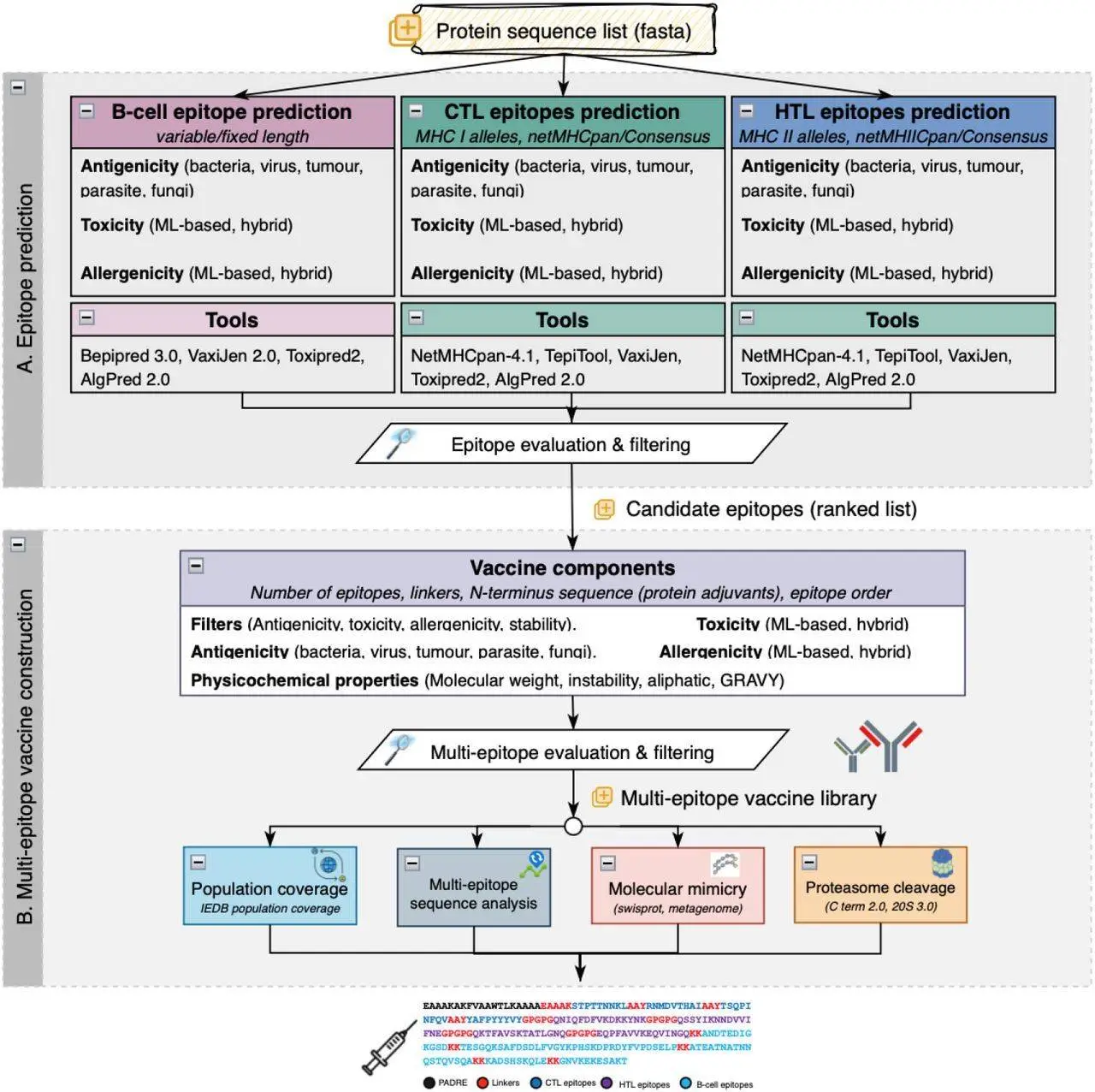
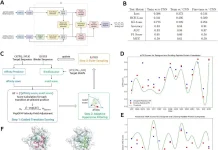
VaccineDesigner is a pioneering web-based server application that uses computational capability to accelerate epitope selection, assessment, and vaccine development. It carries effective algorithms for predicting epitope antigenicity, evaluating safety profiles, and optimizing multi-epitope edifices. VaccineDesigner can integrate splendid strategies for figuring out how extraordinary immune cells (B cells, cytotoxic T cells, and helper T cells) react to unique MHC peptides. This makes it attainable to make vaccines in a way that has in no way been feasible earlier, making the technique more useful.
Crafting Tomorrow’s Shield: The Modular Architecture of Vaccine Design
VaccineDesigner offers a customizable template to optimize vaccine epitopes. Its key trends include:
Tool Integration: Leverages numerous gears for epitope estimation, authentication, and assortment, making an allowance for the amalgamation of numerous methods to enhance vaccine design.
Intuitive Web Interface: Provides a consumer-friendly net platform wherein customers can stipulate parameters that encompass the huge style of epitopes focused on B cells, CTL, and HTL, similarly to choosing out linkers and adjuvants.
Control Over Vaccine Sequences Creation: Offers manipulation over the formation of vaccine sequences, permitting researchers to pick particular epitopes, linkers, and adjuvants based totally on their research objectives.
Vaccine Selection Process: VaccineDesigner dynamically evaluates and ranks vaccines. It prioritizes sequences with immoderate antigenicity, low toxicity, low allergenicity, and genuine stability. This ensures that the maximum number of propitious candidates is determined for similar development.
Adaptive and Evolving Platform: Vaccine Designer’s modular layout makes it flexible and capable of combining new capabilities. This shall be preserved with cutting-edge advances in developing anti-epitope tablets.
VaccineDesigner Reigns Supreme, Researchers Assert
Compared to one-of-a-kind structures, VaccineDesigner stands out in numerous key approaches:
- Unlike Vaxign2, VaccineDesigner can perform quantitative protein assessment.
- Provides more particular predictions than iVAX Suite by way of predicting B lymphocyte cell epitopes using awesome alleles.
- This open platform helps multi-epitope vaccine development beyond Vacceed’s command line.
- Vaccine Designer’s handy interface simplifies the arrival of vaccine epitopes, setting them apart from the Immune Epitope Database (IEDB).
Unlocking Insights
Researchers proved the skills of their technique by employing the use of protein sequences from Staphylococcus aureus, specifically Atl and IsdA.
B lymphocyte epitope predictions: Software is used to perceive epitopes, which are places of proteins identified through the immune system. A total of 123 epitopes have been placed in Atl and 136 in IsdA. After evaluating toxicity, hypersensitive reaction, and antigenicity, thirteen epitopes have been selected for inclusion inside the vaccine.
CTL epitope prediction: Ninety-six epitopes in Atl and eighteen in IsdA were tested for their capacity to bind MHC elegance I alleles. Finally, six epitopes had been decided on for vaccine use primarily based on toxicity, allergy, and antigenic properties.
HTL epitope prediction: 193 HTL epitopes from Atl and fifty HTL epitopes from IsdA were tested for binding to MHC elegance II molecules. After toxicity, nineteen epitopes stayed.
Multi-epitope vaccine format: The viable epitopes are mixed in the following order: CTL, HTL, and B cells. As a result, 864 antibodies were generated.
Empowering Users: Evaluating Sequence Parameters Made Simple
Population Coverage Assessment: The IEDB Population Coverage tool may be used to evaluate the effectiveness of vaccine sequences in protecting distinct populations. It lets researchers pick out antigens and decide the coverage of T-cell epitopes from the vaccine sequences across various geographic regions.
Molecular Mimicry: Users can use BLASTp to evaluate vaccine proteins to SwissProt database proteins and metagenomic proteins. This facilitates discovering similarities that ensure the vaccine can trigger an immune reaction without causing autoimmune reactions.
Proteasome Cleavage: NetChop3.1 software predicts which immune machine will break up (cleave) vaccine proteins. This data helps researchers choose vaccine candidates that might be the most likely to be identified with the aid of the immune system.
Multi-Epitope Scrutiny: Users can check if their vaccine collection incorporates any new epitope parts of the protein that cause the immune response.
Enhancing Vaccine Development Globally
VaccineDesigner, offering its modular layout and consumer-pleasant interface, empowers researchers globally to boost vaccine improvement. It aids in enhancing vaccine efficacy and ensuring protection. VaccineDesigner transforms the process by imparting superior evaluation and equipped epitope prediction, making vaccine development swiffer, extra low-priced, and more logical.
Looking Ahead
In an era plagued by health crises, VaccineDesigner is a beacon of hope. It opens new avenues for vaccine development and sickness mitigation through epitope-primarily based design and modern-day generation. Working collectively and maximizing VaccineDesigner’s potential will pave the way for a healthier future for all.
Article source: Reference Article | VaccineDesign is accessible at the Website | Source code available at GitHub
Important Note: bioRxiv releases preprints that have not yet undergone peer review. As a result, it is important to note that these papers should not be considered conclusive evidence, nor should they be used to direct clinical practice or influence health-related behavior. It is also important to understand that the information presented in these papers is not yet considered established or confirmed.
Follow Us!
Learn More:
Anshika is a consulting scientific writing intern at CBIRT with a strong passion for drug discovery and design. Currently pursuing a BTech in Biotechnology, she endeavors to unite her proficiency in technology with her biological aspirations. Anshika is deeply interested in structural bioinformatics and computational biology. She is committed to simplifying complex scientific concepts, ensuring they are understandable to a wide range of audiences through her writing.