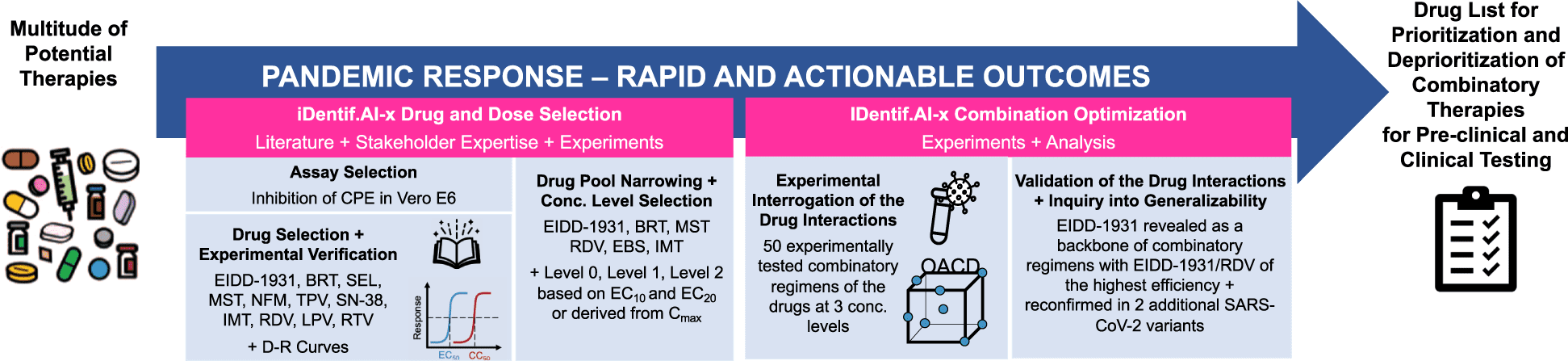
Scientists from the National University of Singapore and DSO National Laboratories, Singapore develop IDentif.AI-x, a pandemic readiness platform powered by artificial intelligence for the rapid prioritization of COVID-19 optimized combination therapy regimens.
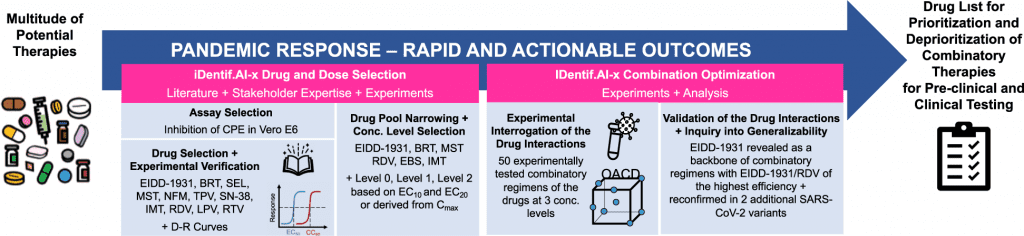
Image Source: The IDentif.AI-x pandemic readiness platform: Rapid prioritization of optimized COVID-19 combination therapy regimens.
By combining a prospective, experimental validation of multi-drug efficacy on a SARS-CoV-2 live virus and Vero E6 assay with a quadratic optimization workflow, IDentif.AI-x, a clinically actionable artificial intelligence platform, was used to quickly identify and prioritize the best combination therapies against COVID-19.
Six candidate drugs were chosen from a starting pool of 12 candidate drugs that were created in collaboration with a group of infectious disease clinicians. These six drugs were then examined in 50 combination regimens at three dosing levels each, representing 729 possible combinations.
EIDD-1931 was identified as a strong candidate for various drug combinations by IDentif.AI-x, which also identified several clinically relevant drug interactions that were later verified in SARS-CoV-2 variants B.1.351 (Beta) and B.1.617.2 (Delta).
In an actionable method toward quickly optimizing combination therapy after pandemic onset, IDentif.AI-x prioritized promising drug combinations for clinical translation and may be instantaneously changed and re-executed with a new pool of promising treatments.
Yield Combinations from True Optimization
The development of COVID-19 drugs has mostly concentrated on repurposing, either through a single agent or combination therapy.
The repurposed candidates’ clinical trial results to date have been inconsistent. Even if many monotherapies fail to produce significant therapeutic benefits, their use in carefully planned medication combinations may produce unexpected success.
It is difficult for conventional antiviral susceptibility testing to address this issue. The intricacy of drug selection and dose-dependent drug synergy must thus be resolved by creating innovative techniques that take advantage of unanticipated drug interactions.
The choice of drug and dose is so intertwined with the choice of candidate therapies that true optimization frequently results in combinations of unanticipated but clinically useful drugs and doses.
Sadly, concurrent drug and dose optimization is an impossible obstacle. Twelve drugs, for instance, evaluated at three dose levels yield nearly 500,000 potential combinations.
Numerous significant methods for predicting synergy and analyzing higher-order pharmacological interactions have been investigated.
Development of the IDentif.AI Platform
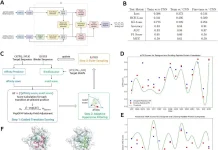
The scientists created the IDentif.AI platform, an AI-based approach for rapid combination therapy development, to address the issue of ensuring clinical actionability of the combination design output. IDentif’s initial combination. AI depicted that the biological response to therapy can be represented as a smooth surface using neural networks.
The coefficients of a second-order algebraic function were calculated through a limited number of prospective trials in further research to resolve this surface, which may quickly discover optimal combinations.
Later, in prospective human trials on infectious disease, cancer treatment, transplant medicine, and other reasons, this link was confirmed.
In silico modeling, synergy prediction, and algorithm training are all performed by IDentif.AI without the usage of pre-existing data. Instead, it chooses the medications and dosages that make up globally optimum combination regimens using experimental testing.
Based on the prevention of SARS-CoV-2-led cytopathic effects mediated by unanticipated medication interactions, our most recent IDentif.AI investigation identified the top-ranked combinations.
Although the use of AI has aided in the quick identification of potential therapeutic drugs for COVID-19, it is crucial that an effective AI platform can easily support a rapid response along the pandemic timeline, given the pandemic’s rapid evolution and the surge in knowledge generation about drugs, targets, and pathways over time.
Technical adaptability of the AI platform and clinical acceptability of the AI-based discoveries are desirable characteristics of a pandemic-ready platform.
An AI platform’s technical adaptability enables its timely, resource-efficient, and flexible application at various pandemic stages.
Additionally, by including features that increase the clinical acceptability of the AI platform, such as incorporating clinical expertise into the workflow, physiological applicability, and taking into account practical implementation aspects of the suggested therapies, it is possible to support quick and widespread clinical implementation of the study’s findings.
As a result, after the initial demonstration, the scientists expanded the workflow and further improved the platform to create IDentif.AI-x, which is now available.
A Pandemic Ready Platform
By utilizing IDentif.AI-x to assess a beginning pool of candidate medicines that have been or are being studied in multiple COVID-19 clinical settings and in conjunction with the clinical community, this study aims to demonstrate IDentif.AI-x as a pandemic-ready platform.
The following therapies were considered as potential treatments:
- EIDD-1931 (a metabolite of EIDD-2801 (molnupiravir)),
- Baricitinib (BRT),
- Ebselen (EBS),
- Selinexor (SEL),
- Masitinib (MST),
- Nafamostat mesylate (NFM),
- Telaprevir (VX-950; TPV),
- SN-38 (a metabolite of irinotecan)
- Imatinib mesylate (IMT),
- Remdesivir (RDV),
- Lopinavir (LPV), and
- Ritonavir (RTV)
IDentif.AI-x implementation on a propagated, original live SARS-CoV-2 strain was finished within three weeks.
The Endpoint
There are also certain technical constraints with the IDentif.AI-x approach. It was created with quick optimization and clinical actionability in mind, and you can incorporate additional ways to deal with them.
First, a quadratic relationship between the efficacy/cytotoxicity responses and the IDentif.AI-x interaction space interrogation is assumed.
The two-drug combinations constitute the majority of the optimal combinations that were studied in the paper, allowing for quick identification of the most important medications and their partners from a sizable drug combination search pool.
Similar to other studies, future research on more intricate combinatorial therapeutic techniques, including four- or five-drug combinations, will probably necessitate some reconciliation of higher-order interactions.
Second, a small number of dosage ratios were examined. The finding that the same pharmacological combination may exhibit opposing interactions at two different ratios emphasizes the significance of adjusting drug dosages concurrently with their combinations.
The observed findings do, however, imply that additional preclinical and clinical dosing optimization may reveal the full potential of the identified combination therapies in terms of their synergistic potency (i.e., advantageous dose reduction) and synergistic efficacy interactions (i.e., beneficial increase in maximum efficacy).
When they become available, more correlation studies with clinical trial results would help determine whether IDentif.AI-x can be used to make go/no-go choices on the combination regimens it has identified.
The IDentif.AI-x methodology has produced encouraging results in its current iteration; however, further development of IDentif.AI-x and potential integration with other methodologies may further increase its clinical applicability.
The use of IDentif.AI-x for the expedient optimization and prioritizing of combination therapy regimens against COVID-19 is reported in the given paper.
The EIDD-1931/RDV, EIDD-1931/BRT, and EIDD-1931/MST regimens were identified by the IDentif.AI-x optimization method as potential candidates for further analysis and development.
To create these combinations, IDentif.AI-x did not rely on extensive scientific literature networks, pre-existing databases, or in silico modeling. Instead, it used information from carefully thought-out drug-dose variations and prospectively completed trials to guide the optimization process and support current COVID-19 pandemic prevention initiatives.
The positive results of this research encourage the development of IDentif.AI-x for a wide range of applications in combating antimicrobial resistance and improving intervention employing antiviral, antibiotic, and antifungal medicines.
Article Source: Blasiak, A., Truong, A.T.L., Remus, A. et al. The IDentif.AI-x pandemic readiness platform: Rapid prioritization of optimized COVID-19 combination therapy regimens. npj Digit. Med. 5, 83 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41746-022-00627-4
Learn More About Bioinformatics:
Top Bioinformatics Books ↗
Learn more to get deeper insights into the field of bioinformatics.
Top Free Online Bioinformatics Courses ↗
Freely available courses to learn each and every aspect of bioinformatics.
Latest Bioinformatics Breakthroughs ↗
Stay updated with the latest discoveries in the field of bioinformatics.
Tanveen Kaur is a consulting intern at CBIRT, currently, she's pursuing post-graduation in Biotechnology from Shoolini University, Himachal Pradesh. Her interests primarily lay in researching the new advancements in the world of biotechnology and bioinformatics, having a dream of being one of the best researchers.