Functional proteomics makes the identification of new biomarkers and treatment targets easier by offering vital insights into cancer mechanisms. By combining information from over 900 samples from the Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia and nearly 8000 patient samples from The Cancer Genome Atlas, researchers have created a comprehensive cancer functional proteomics database employing reverse phase protein arrays. All of the main cancer characteristic pathways are covered by the carefully selected panel of about 500 excellent antibodies in our dataset. Researchers from The University of Texas present DrBioRight 2.0, an intelligent bioinformatics platform driven by cutting-edge big language models, to improve the resource’s usability and analytical capability. DrBioRight gives researchers the ability to examine protein-centric cancer omics data, carry out sophisticated analyses, display findings, and have interactive conversations in natural language.
Introduction
The creation of cancer omics data has advanced significantly over the last ten years, especially when it comes to the DNA and RNA levels in patient tumors. Initiatives such as the Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia (CCLE) and The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) have been essential in this revolutionary period. However, there is still a significant knowledge vacuum regarding the translational and post-translational landscape of human malignancies, particularly when it comes to numerous cancer lineages. A wide population can benefit from the large-scale functional proteomics data of cancer samples that reverse phase protein arrays (RPPAs) offer.
Looking into Paper’s Work
TCPA’s immediate usefulness is restricted by two significant issues. First, only about 200 protein markers were covered in the earlier RPPA data. Second, there is little room for user-defined analysis in the data portal, which only offers a few established analytical modules. Researchers have recently increased the number of high-quality antibodies in our RPPA protein panel to about 500 to address these issues. By combining information from both TCGA and CCLE samples, this extension has made it possible to create a thorough, superior pan-cancer functional proteomics compendium known as RPPA500.
Researchers present DrBioRight 2.0, a state-of-the-art chatbot driven by large language models (LLMs), in addition to our enlarged proteome dataset. The goal of this tool is to simplify technological obstacles so that complicated omics data may be analyzed with ease. Natural language searches are simple to use and allow users from various backgrounds to access, analyze, and visualize data smoothly.
Architecture of DrBioRight
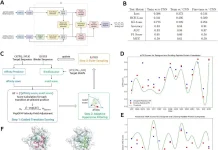
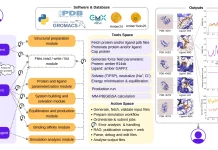
Three essential elements make up the system architecture of DrBioRight 2.0: an interactive chat interface, a back-end analytics module driven by LLM, and a No-SQL database. Users can choose an illness and connect pertinent multi-omics data to their project space for study thanks to the system architecture. Based on a chain-of-thought methodology, the back-end LLMs provide a logical flow and forecast user intent. Code is reviewed and validated by the platform, which fixes typical mistakes like missing libraries or conflicting package versions. The results are shown in an easy-to-use chat interface, and users can rate the analytical results. To improve LLMs, reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) is used in conjunction with expert manual evaluations to guide iterative refinements.
More About DrBioRight
DrBioRight creates an interactive heatmap by dynamically processing the data and triggering the relevant heatmap plugin. Like other interactive plugins researchers used, the heatmap plugin handles big datasets effectively. It provides a whole worldwide overview in addition to a plethora of tools (including search, zoom in/out, selection, 2D/3D scatter plots, pathway mapping, and connection to external sites) to enable efficient data study. The data is subsequently extracted by DrBioRight, which also conducts the necessary statistical analysis and displays the findings in an understandable scatter plot.
DrBioRight is a special analytical tool that provides unmatched customization and versatility in data processing. Using Kaplan-Meier plots for visualization, users can perform a survival analysis by looking at the relationship between a protein and patient survival time.
To set itself apart, DrBioRight provides users personalized interactions with the chatbot. For example, users can alter the colors in a plot or look into particular relationships with male or female patients. For local analysis, users can also ask the chatbot to provide a summary of the findings and download the project report as an R markdown file.
Conclusion
A significant breakthrough for biomedical researchers, DrBioRight 2.0 hits significant benchmarks in the analysis of cancer proteomics data. For frequently utilized cell lines and cancer patient cohorts, it expands the protein space, offering a useful resource. The LLM-empowered chatbot provides a user-friendly, adaptable, and highly configurable platform that reduces barriers to entry and makes it possible for researchers with various backgrounds to analyze data effectively. Deep integration between the data resource and LLMs increases the resource’s usefulness by improving customization choices, speeding up the user-developer feedback loop, and enhancing data accessibility. Data analysis and sharing platforms will undergo a paradigm shift as a result of DrBioRight’s special mix of an extensive data supply and cutting-edge LLMs, creating a whole ecosystem designed specifically for biomedical researchers.
Article Source: Reference Paper | The compiled software and detailed description of the code’s functionality is available on the website.
Disclaimer:
The research discussed in this article was conducted and published by the authors of the referenced paper. CBIRT has no involvement in the research itself. This article is intended solely to raise awareness about recent developments and does not claim authorship or endorsement of the research.
Follow Us!
Learn More:
Deotima is a consulting scientific content writing intern at CBIRT. Currently she's pursuing Master's in Bioinformatics at Maulana Abul Kalam Azad University of Technology. As an emerging scientific writer, she is eager to apply her expertise in making intricate scientific concepts comprehensible to individuals from diverse backgrounds. Deotima harbors a particular passion for Structural Bioinformatics and Molecular Dynamics.