Google’s Health AI-Developed Foundations (HAI-DEF) has released an updated version of MedGemma (v1.5), an open-source generative AI model with enhanced capabilities in medical imaging and speech recognition. When integrated with MedASR—a newly developed medical speech-to-text model fine-tuned for healthcare dictation—the system operates seamlessly to support complex medical reasoning tasks.
Given the pace at which AI adoption in healthcare is taking place, Google is also positioning itself as a key player by releasing open-source medical AI models.
MedGemma 1, the original release by Google’s Health AI Developer Foundations (HAI-DEF) program, was a starting point that could be deployed and scaled easily on Google Cloud Vertex AI. It was adapted to personal medical imaging use cases, but wasn’t directly used in hospitals; it still showed huge uptakes with millions of downloads and hundreds of variants shared on Hugging Face. Google collected direct feedback from this community activity for what worked, what needed improvement, and which medical imaging tasks were in demand.
The newer updated version, MedGemma 1.5, was guided by that feedback, and now shows improved ability to handle multiple medical imaging modalities, from scans like CT, MRI, to chest X-rays, and goes beyond to handle textual medical data such as clinical questions.
A Kaggle hackathon was launched alongside MedGemma 1.5 with hefty prizes to encourage developers to build real healthcare applications using the model.
A deep dive into MedGamma 1.5: Case Studies
According to Google, MedGemma 1.5 is the first public release of an open-source multimodal LLM that can handle high-dimensional medical data and still interpret 2D images and texts.
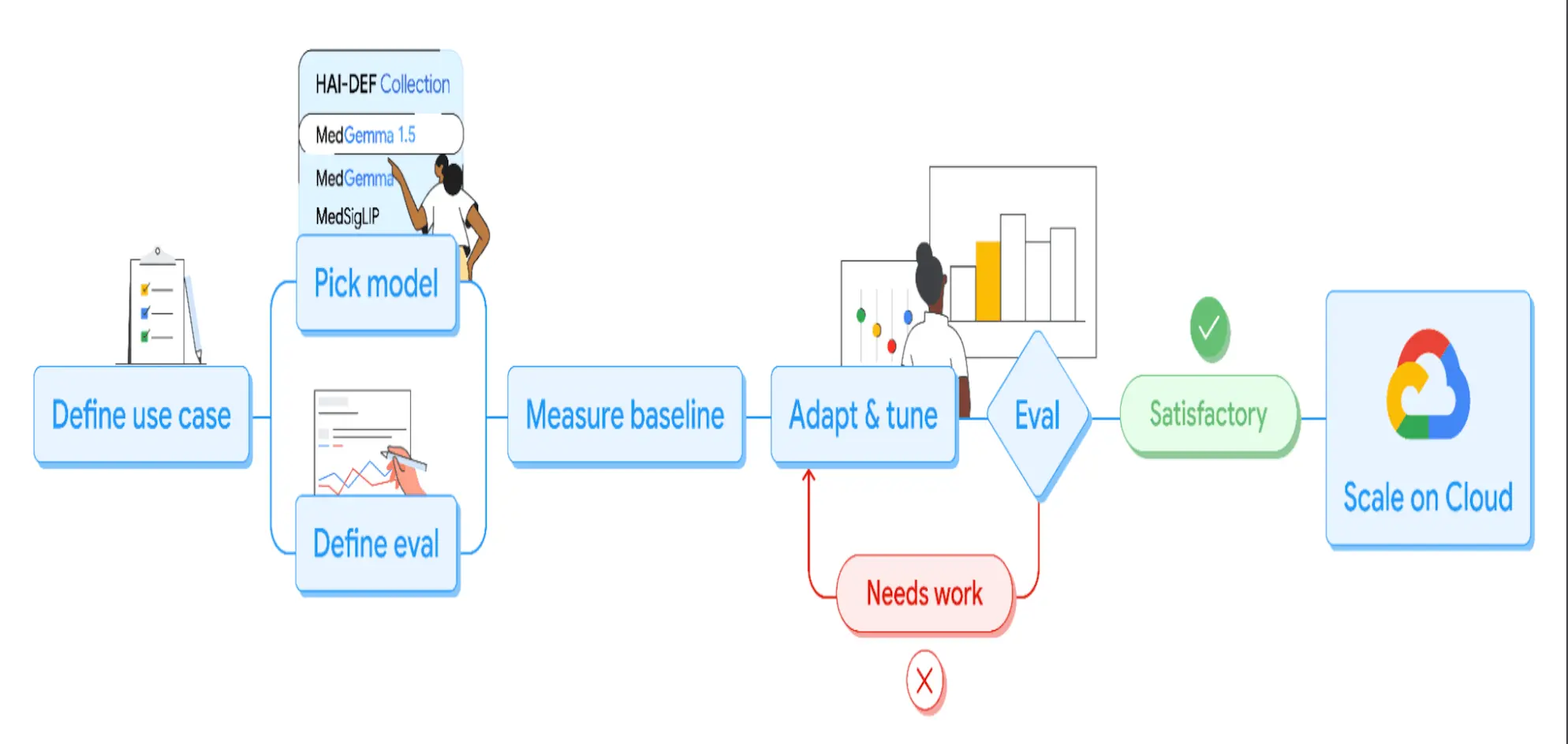
Different variants of MedGemma are accessible through the Hugging Face Collection, making it easier for developers to experiment and deploy both offline lightweight tasks or heavier text-based workloads.
Google has also released tutorial notebooks to help developers experiment with different imaging tasks. These tutorials show how to feed CT/MRI slices or histopathology patches into MedGemma along with a task prompt. As a result, health tech startups and independent developers worldwide are now using MedGemma to accelerate research and product development.
Use Case 1: Qmed Asia & Malaysia’s Ministry of Health:
Qmed Asia integrated MedGemma into askCPG, a conversational interface that provides easy access to Malaysia’s 150+ clinical practice guidelines (CPGs).
The Ministry of Health Malaysia reports that askCPG makes working with guidelines more practical for daily clinical decision making. Moreover, its ability to handle medical images alongside text has been well-received in early-stage deployments, showing its usefulness in real-world clinical workflows.
Use Case 2: Taiwan’s National Health Insurance Administration (NHIA)
NHIA oversees healthcare policy and insurance coverage for the country, so its use of MedGemma is at a national scale. They applied MedGemma to evaluate preoperative assessments for lung cancer surgery.
Here, MedGemma was used to extract key data from a massive dataset of over 30,000 pathology reports and other unstructured medical data. Using the output, NHIA performed statistical analyses to better understand patients’ preoperative medical conditions.
How MedASR Complements MedGemma for Medical Text Interpretation
According to Google, speech provides a more natural and efficient way to interact with AI systems when it comes to clinical workflows, as text is the main interface for large language models today, but in medicine, verbal communication is essential as doctors often dictate notes, radiology findings, or lab interpretations rather than typing them, be it in live conversations between patients.
To bridge the gap between spoken medical communication and text-based AI systems, MedASR was developed as a speech-to-text model working as a transcriber. Instead of typing, a doctor can speak instructions that MedASR converts into text for MedGemmma to process hand in hand.
When compared against Whisper large-v3, a general ASR model, MedASR showed a word error rate (WER) of 5.2% for chest X-ray dictations; 58% fewer errors than whisper at 12.5%. When it comes to diverse medical dictation (multiple specialities & speakers), MedASR again had a WER of 5.2% while that of whisper had 28.2%; about 82% fewer errors.
This indicates the higher accuracy of MedASR in handling medical speech than general-purpose ASR systems.
Important Note
Both MedGemma and MedASR are research and development tools, not ready-to-use clinical systems. They require validation, adaptation, and fine-tuning before being applied in real-world medical practice. Outputs are preliminary and not intended to directly guide diagnosis or treatment.
Article Source: Reference Article.
Disclaimer:
The research discussed in this article was conducted and published by the authors of the referenced paper. CBIRT has no involvement in the research itself. This article is intended solely to raise awareness about recent developments and does not claim authorship or endorsement of the research.
Follow Us!
Learn More:
Saniya is a graduating Chemistry student at Amity University Mumbai with a strong interest in computational chemistry, cheminformatics, and AI/ML applications in healthcare. She aspires to pursue a career as a researcher, computational chemist, or AI/ML engineer. Through her writing, she aims to make complex scientific concepts accessible to a broad audience and support informed decision-making in healthcare.